Understanding Omnichain Framework
High Level Architecture
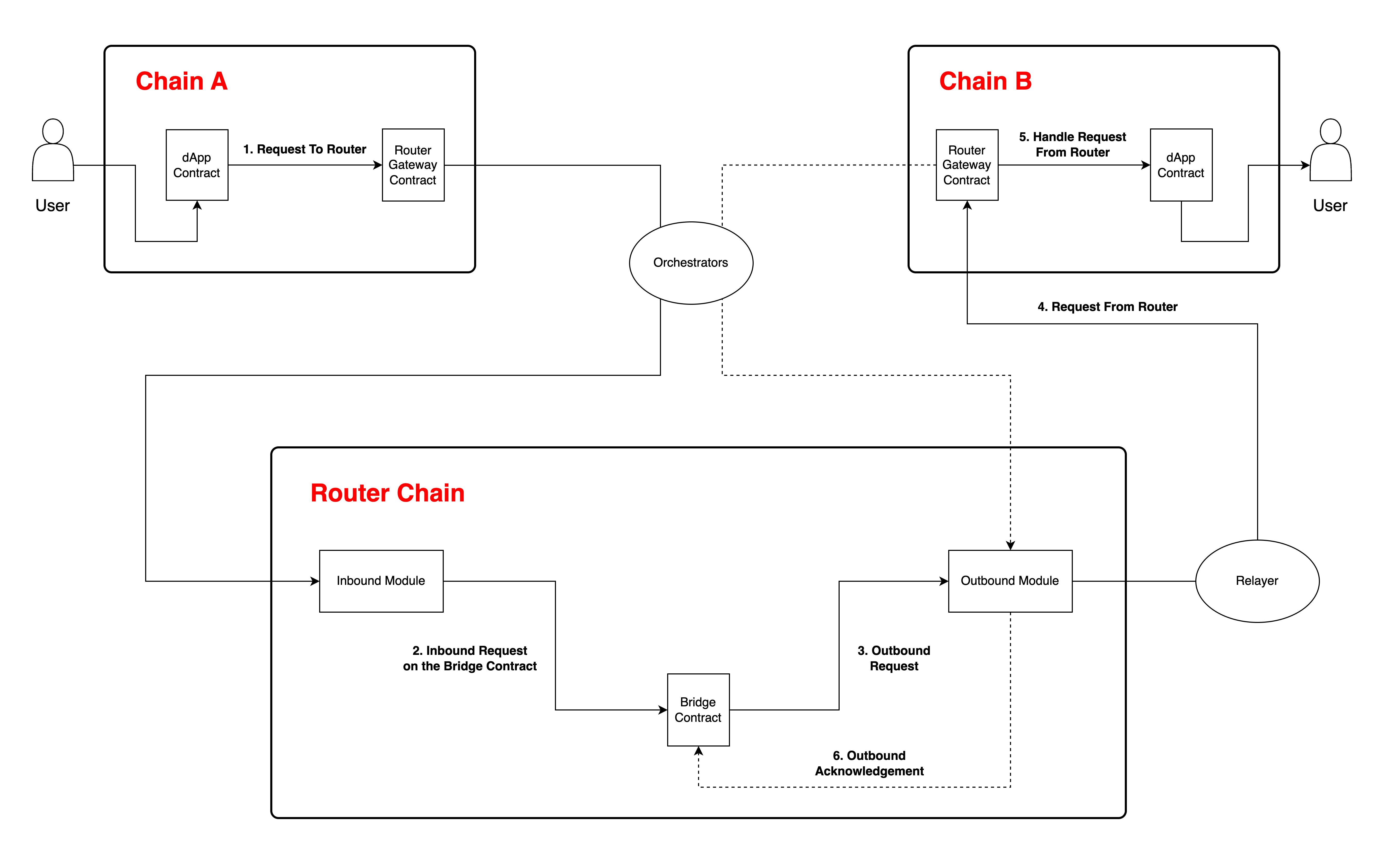
Any cross-chain request between two third-party chains is divided into two independent flows - Inbound and Outbound.
Warning: Not all inbound requests need to have a corresponding outbound request, and vice versa. In any cross-chain request with the Router chain as the destination chain, there won't be any outbound request. Similarly, any cross-chain request originating from the Router chain won't have any inbound request.
Inbound Workflow
Step 1) A user initiates a cross-chain action on an application's smart contract on the source chain.
Step 2) The application contract then calls the iSend() function on the Router Gateway contract with the relevant parameters.
Step 3) The Gateway contract on the source chain emits an event that is listened to by the orchestrators on the Router chain.
Step 4) After validating the event with the help of the attestation module, the inbound module passes the event to the application's bridge contract on the Router chain, where it can implement its custom business logic.
Outbound Workflow
Step 1) After the transaction initiated by the bridge contract is mined on the Router chain, the outbound module picks up the outbound request generated by the bridge contract.
Step 2) The outbound module collects and persists all the signatures given by orchestrators to validate the outbound request.
Step 3) Once the majority voting power is achieved, the relayer polling the outbound requests of that particular bridge contract picks up the transaction and forwards the event to the Router Gateway contract on the destination chain.
Step 4) The Gateway contract on the destination chain calls the iReceive() function on the application contract on the destination chain.
Step 5) The application contract on the destination chain will take appropriate actions based on the data transferred.
Step 6) After the iReceive() function execution is complete on the destination chain, the destination chain's Gateway contract emits an acknowledgment event that is listened to by the orchestrators on the Router chain.
Step 7) The ack is then submitted to bridge contract ensuring the execution of Outbound Request. Upon receiving the ack, the bridge contract can mark the status of outbound request as completed and take required actions.